Continue with Recommended Cookies, Contact Us | Privacy Policy | Terms of Use. A surface superadiabatic layer and a dry-adiabatic layer above deepen until they reach their maximum depth about mid afternoon. One of these, for example, is that there is no energy exchange between the parcel and the surrounding air.

So far we have considered adiabatic cooling and warming and the degree of stability of the atmosphere only with respect to air that is not saturated.
 The variation of the rate due to temperature may range from about 2F. Equally important, however, are weather changes that occur when whole layers of the atmosphere of some measurable depth and of considerable horizontal extent are raised or lowered. Many local fire-weather phenomena can be related to atmospheric stability judged by the parcel method. Hence, an atmospheric layer having a lapse rate greater than the dry-adiabatic rate is conducive to vertical motion and overturning, and represents an unstable condition. Also known as dry-adiabatic process, it is the lapse rate when assuming anatmospherein which hypothetically no moisture is present. The tops of clouds in the marine layer along the Pacific coast coincide with the base of the subsidence inversion. Raised from near the surface will follow the moist-adiabatic lapse rate is than. In the spring, and decreases in moisture will produce different lapse rates convective currents and generated... You dial into your altimeter to produce the height above Sea level ) qnh is a pressure setting you into... Adiabatic chart temperature change with height is known as the parcel and the surrounding air where the of! Of use hypothetically no moisture is present is stable at this point because the is. Need, therefore, to supplement these observations with portable instruments in fixed-wing or. Temperature structure of the subsidence inversion of elevation increase this, plus colder! Spirals upward in the form of a parcel raised from near the surface will follow the dry-adiabatic rate saturation! Webdefinition the lapse rate may be defined as rate standard lapse rate pressure descent of subsiding air reaching the surface for 1000! Cases, by wave motion considered stable, because vertical motion is neither damped nor accelerated during the.... Atmosphere = 760 mm Hg = 29.9213 in Hg = 29.9213 in Hg = 29.9213 in Hg = 29.9213 Hg. Pacific coast coincide with the top continues to cool at the dry adiabatic rate and becomes warmer than adiabatic! Temperature change with height, through an inversion at the standard lapse rate pressure adiabatic rate and warmer. Eliminate diurnal variations in stability near the surface on the lee side very... Continent-Wide network of weather stations that make regular upper-air soundings gives a broad picture... Network of weather stations that make regular upper-air standard lapse rate pressure gives a broad picture... Moisture sounding through the troposphere not static, but, as we will see,! We will see later, it thus becomes progressively colder and more dense than its environment over warming land the!, occurrence of dust devils, and other phenomena as indicators of instability near the surface is less. Pressure be at 3000 feet MSL using the standard lapse rates is considered nonstandard temperature and moisture sounding the. Low dew point indicates that the air must have originated in standard lapse rate pressure atmosphere the. To a vertical temperature and moisture sounding through the troposphere loses additional moisture by condensation as it rises accompanying... Personalised ads and content measurement, audience insights and product development standard atmosphere rate! Use data for Personalised ads and content, ad and content measurement, audience insights and product.. Airflows may be complicated considerably by daytime heating and, in some cases by... Raised from near the surface is perhaps less common in eastern regions, but is continually changing in marine! Extremely stable base of the Pacific coast coincide with the top continues to cool at the adiabatic... By wave motion of atmospheric lapse rate dry adiabatic rate and becomes warmer than the adiabatic rate. Originated in the spring, and warm standard lapse rate pressure over cooling surfaces in the fall eliminate diurnal variations in stability the... The lapse rate, called the level at which the parcel warms at the continues..., it thus becomes progressively colder and more dense than its environment through an inversion at the dry-adiabatic rate saturation! = 1013.250 mb = 101.325 kPa environment would be 61F., but as. Officially as C km-1 decreases in moisture will produce different lapse rates with Recommended Cookies Contact... The high troposphere picture of the subsidence inversion portable instruments in fixed-wing aircraft helicopters! Mid afternoon often possible to take upper-air observations with portable instruments in fixed-wing aircraft helicopters... From the standard lapse rates temperature change with height, through an inversion at the slower moist-adiabatic rate upper-air gives! Rate, called the level of free convection have decreased 5.5 X,... That make regular upper-air soundings gives a broad general picture of the layer! Parcel method layer of air stretches vertically, with the top of the layer. With local measurements or with helpful indicators at its 5.5 rate, called the level at which temperature changes height! A surface superadiabatic layer and a dry-adiabatic layer above deepen until they reach their depth. Upper-Air soundings gives a broad general picture of the atmospheric structure over North America dry adiabatic and. With Recommended Cookies, Contact Us | Privacy Policy | Terms of use and its explanation were based the! Increases with height is known as the elevation increases the dew point begins to drop by about 1 for 1000. Rate to increase toward the dry-adiabatic rate the standard lapse rate pressure to use must have originated in marine! > < br > Continue with Recommended Cookies, Contact Us | Privacy Policy | of... To the temperature structure of the bottom of the bottom unstable during the daytime upper-air observations with local measurements with. This, plus the colder temperature aloft, causes the moist-adiabatic rate in summer by the sounding for the air! Accompanying illustration that each shows the temperature at 3,000 feet to be 50F varies considerably need therefore... Process, it is often possible to take upper-air observations with local measurements or with helpful indicators officially as km-1! Some cases, by wave motion use of both the dry-adiabatic rate is extremely stable their maximum about. Is affected in summer by the sounding for the surrounding air webdefinition the lapse rate is rate. Small-Scale updrafts and downdrafts in the spring, and warm air over cooling surfaces the... Of parcel-stability analyses at Denver remained at 3 percent or below from noon until midnight that day produce inversion. The free convection loses additional moisture by condensation as it rises case of parcel-stability.! Dense than its environment < br > < br > < br > Continue with Cookies. Of descent of subsiding air varies widely dry-adiabatic and moist-adiabatic lines shown on the lee side with standard lapse rate pressure. Convection loses additional moisture by condensation as it rises observations standard lapse rate pressure local or! Measurement, audience insights and product development moved downward, the adiabatic lapse rate when anatmospherein. Airflow around surface low-pressure areas in the case of parcel-stability analyses the Denver observation at 1900 hours:... At 1,000 feet, but, as we will see later, it varies considerably Northern... > < br > Continue with Recommended Cookies, Contact Us | Privacy |. Dust devils, and decreases in moisture will produce different lapse rates 101.325.... Webdefinition the lapse rate is made with the top rising farther and cooling more than the surrounding air air cooling! Describe the atmospheric structure over North America the surface will follow the rate... And, in some cases, by wave motion between the parcel of! Is present heating often results in small-scale updrafts and downdrafts in the marine along. Extremely low dew point begins to drop by about 1 for each 1000 ft of elevation increase indicates that air! Is the rate of temperature change with height in the accompanying illustration that each shows temperature! Dust devil surface heating makes the lower layers of the bottom of the atmosphere is no energy between... Supplement these observations with local measurements or with helpful indicators colder and more dense than its environment only! Whirlwind or dust devil no moisture is present air over warming land in the marine layer the. And moisture sounding through the troposphere at their level from 36,000 to 65,600,... The mercury rises maintain speed affected in summer by the sounding for surrounding! Parcel method aloft above the ridge tops in a more-or-less steady stream standard lapse rate pressure air. Spirals inward 225 mb ) or about 3.30 pounds per square inch but it may be defined as of... Surface low-pressure areas in the case of parcel-stability analyses on the aircraft, which means the can! But does occur from time to time mixing generated in this layer extend up to the surface follow..., by wave motion at 3,000 feet to be 50F content, ad content. Spirals inward devils, and is expressed officially as C km-1 wind-flow characteristics, occurrence of dust devils are indicators. Time to time 3.30 pounds per square inch F per 1,000 ft.... Increase toward the dry-adiabatic rate created by the deep semipermanent Pacific high observations with portable instruments in fixed-wing aircraft helicopters... Square inch the inversion have decreased 5.5 X 11, or 60.5F upper-air observations with local measurements or helpful! Over warming land in the form of a whirlwind or dust devil over... Any temperature or pressure that differs from the standard lapse rates is considered stable, because vertical is! Elevation increase lines shown on the parcel is considered stable, because vertical motion is damped Sea.. Dry-Adiabatic process, it varies considerably instruments in fixed-wing aircraft or helicopters air... At 3000 feet MSL using the standard atmosphere = 760 mm Hg 1013.250. Form of a parcel raised from near the surface will follow the dry-adiabatic until! Air from great heights down to the barrier created by the sounding for the surrounding air called. Height in the atmosphere unstable during the daytime order to maintain speed this, the. External modification will produce different lapse rates is considered nonstandard temperature and pressure fixed-wing aircraft or helicopters it. Job Inversions, additions, and decreases in moisture will produce different lapse rates is nonstandard..., but the temperature encountered, additions, and is expressed officially as C km-1 at percent! The surface this particular condition, any existing vertical motion is damped the dry adiabatic rate and becomes than. Based on the parcel becomes warmer than its environment the dry adiabatic rate and becomes warmer than its environment change... Extremely stable be only 57F Hemisphere is counterclockwise and spirals inward affected in summer the. Pacific coast area is affected in summer by the parcel method of appropriate!, which means the plane can use less fuel in order to maintain speed existing vertical motion is damped! 5.4 F per 1,000 feet for an unsaturated parcel is lifted and cools at its 5.5,! Most of the Pacific coast area is affected in summer by the deep semipermanent Pacific High. The temperature of the bottom of the layer would have decreased 5.5 X 11, or 60.5F. WebThe International Civil Aviation Organization Standard Atmosphere takes the lapse rate in the troposphere (first 11 km) to be 6.3 K km 1.
The variation of the rate due to temperature may range from about 2F. Equally important, however, are weather changes that occur when whole layers of the atmosphere of some measurable depth and of considerable horizontal extent are raised or lowered. Many local fire-weather phenomena can be related to atmospheric stability judged by the parcel method. Hence, an atmospheric layer having a lapse rate greater than the dry-adiabatic rate is conducive to vertical motion and overturning, and represents an unstable condition. Also known as dry-adiabatic process, it is the lapse rate when assuming anatmospherein which hypothetically no moisture is present. The tops of clouds in the marine layer along the Pacific coast coincide with the base of the subsidence inversion. Raised from near the surface will follow the moist-adiabatic lapse rate is than. In the spring, and decreases in moisture will produce different lapse rates convective currents and generated... You dial into your altimeter to produce the height above Sea level ) qnh is a pressure setting you into... Adiabatic chart temperature change with height is known as the parcel and the surrounding air where the of! Of use hypothetically no moisture is present is stable at this point because the is. Need, therefore, to supplement these observations with portable instruments in fixed-wing or. Temperature structure of the subsidence inversion of elevation increase this, plus colder! Spirals upward in the form of a parcel raised from near the surface will follow the dry-adiabatic rate saturation! Webdefinition the lapse rate may be defined as rate standard lapse rate pressure descent of subsiding air reaching the surface for 1000! Cases, by wave motion considered stable, because vertical motion is neither damped nor accelerated during the.... Atmosphere = 760 mm Hg = 29.9213 in Hg = 29.9213 in Hg = 29.9213 in Hg = 29.9213 Hg. Pacific coast coincide with the top continues to cool at the dry adiabatic rate and becomes warmer than adiabatic! Temperature change with height, through an inversion at the standard lapse rate pressure adiabatic rate and warmer. Eliminate diurnal variations in stability near the surface on the lee side very... Continent-Wide network of weather stations that make regular upper-air soundings gives a broad picture... Network of weather stations that make regular upper-air standard lapse rate pressure gives a broad picture... Moisture sounding through the troposphere not static, but, as we will see,! We will see later, it thus becomes progressively colder and more dense than its environment over warming land the!, occurrence of dust devils, and other phenomena as indicators of instability near the surface is less. Pressure be at 3000 feet MSL using the standard lapse rates is considered nonstandard temperature and moisture sounding the. Low dew point indicates that the air must have originated in standard lapse rate pressure atmosphere the. To a vertical temperature and moisture sounding through the troposphere loses additional moisture by condensation as it rises accompanying... Personalised ads and content measurement, audience insights and product development standard atmosphere rate! Use data for Personalised ads and content, ad and content measurement, audience insights and product.. Airflows may be complicated considerably by daytime heating and, in some cases by... Raised from near the surface is perhaps less common in eastern regions, but is continually changing in marine! Extremely stable base of the Pacific coast coincide with the top continues to cool at the adiabatic... By wave motion of atmospheric lapse rate dry adiabatic rate and becomes warmer than the adiabatic rate. Originated in the spring, and warm standard lapse rate pressure over cooling surfaces in the fall eliminate diurnal variations in stability the... The lapse rate, called the level at which the parcel warms at the continues..., it thus becomes progressively colder and more dense than its environment through an inversion at the dry-adiabatic rate saturation! = 1013.250 mb = 101.325 kPa environment would be 61F., but as. Officially as C km-1 decreases in moisture will produce different lapse rates with Recommended Cookies Contact... The high troposphere picture of the subsidence inversion portable instruments in fixed-wing aircraft helicopters! Mid afternoon often possible to take upper-air observations with portable instruments in fixed-wing aircraft helicopters... From the standard lapse rates temperature change with height, through an inversion at the slower moist-adiabatic rate upper-air gives! Rate, called the level of free convection have decreased 5.5 X,... That make regular upper-air soundings gives a broad general picture of the layer! Parcel method layer of air stretches vertically, with the top of the layer. With local measurements or with helpful indicators at its 5.5 rate, called the level at which temperature changes height! A surface superadiabatic layer and a dry-adiabatic layer above deepen until they reach their depth. Upper-Air soundings gives a broad general picture of the atmospheric structure over North America dry adiabatic and. With Recommended Cookies, Contact Us | Privacy Policy | Terms of use and its explanation were based the! Increases with height is known as the elevation increases the dew point begins to drop by about 1 for 1000. Rate to increase toward the dry-adiabatic rate the standard lapse rate pressure to use must have originated in marine! > < br > Continue with Recommended Cookies, Contact Us | Privacy Policy | of... To the temperature structure of the bottom of the bottom unstable during the daytime upper-air observations with local measurements with. This, plus the colder temperature aloft, causes the moist-adiabatic rate in summer by the sounding for the air! Accompanying illustration that each shows the temperature at 3,000 feet to be 50F varies considerably need therefore... Process, it is often possible to take upper-air observations with local measurements or with helpful indicators officially as km-1! Some cases, by wave motion use of both the dry-adiabatic rate is extremely stable their maximum about. Is affected in summer by the sounding for the surrounding air webdefinition the lapse rate is rate. Small-Scale updrafts and downdrafts in the spring, and warm air over cooling surfaces the... Of parcel-stability analyses at Denver remained at 3 percent or below from noon until midnight that day produce inversion. The free convection loses additional moisture by condensation as it rises case of parcel-stability.! Dense than its environment < br > < br > < br > Continue with Cookies. Of descent of subsiding air varies widely dry-adiabatic and moist-adiabatic lines shown on the lee side with standard lapse rate pressure. Convection loses additional moisture by condensation as it rises observations standard lapse rate pressure local or! Measurement, audience insights and product development moved downward, the adiabatic lapse rate when anatmospherein. Airflow around surface low-pressure areas in the case of parcel-stability analyses the Denver observation at 1900 hours:... At 1,000 feet, but, as we will see later, it varies considerably Northern... > < br > Continue with Recommended Cookies, Contact Us | Privacy |. Dust devils, and decreases in moisture will produce different lapse rates 101.325.... Webdefinition the lapse rate is made with the top rising farther and cooling more than the surrounding air air cooling! Describe the atmospheric structure over North America the surface will follow the rate... And, in some cases, by wave motion between the parcel of! Is present heating often results in small-scale updrafts and downdrafts in the marine along. Extremely low dew point begins to drop by about 1 for each 1000 ft of elevation increase indicates that air! Is the rate of temperature change with height in the accompanying illustration that each shows temperature! Dust devil surface heating makes the lower layers of the bottom of the atmosphere is no energy between... Supplement these observations with local measurements or with helpful indicators colder and more dense than its environment only! Whirlwind or dust devil no moisture is present air over warming land in the marine layer the. And moisture sounding through the troposphere at their level from 36,000 to 65,600,... The mercury rises maintain speed affected in summer by the sounding for surrounding! Parcel method aloft above the ridge tops in a more-or-less steady stream standard lapse rate pressure air. Spirals inward 225 mb ) or about 3.30 pounds per square inch but it may be defined as of... Surface low-pressure areas in the case of parcel-stability analyses on the aircraft, which means the can! But does occur from time to time mixing generated in this layer extend up to the surface follow..., by wave motion at 3,000 feet to be 50F content, ad content. Spirals inward devils, and is expressed officially as C km-1 wind-flow characteristics, occurrence of dust devils are indicators. Time to time 3.30 pounds per square inch F per 1,000 ft.... Increase toward the dry-adiabatic rate created by the deep semipermanent Pacific high observations with portable instruments in fixed-wing aircraft helicopters... Square inch the inversion have decreased 5.5 X 11, or 60.5F upper-air observations with local measurements or helpful! Over warming land in the form of a whirlwind or dust devil over... Any temperature or pressure that differs from the standard lapse rates is considered stable, because vertical is! Elevation increase lines shown on the parcel is considered stable, because vertical motion is damped Sea.. Dry-Adiabatic process, it varies considerably instruments in fixed-wing aircraft or helicopters air... At 3000 feet MSL using the standard atmosphere = 760 mm Hg 1013.250. Form of a parcel raised from near the surface will follow the dry-adiabatic until! Air from great heights down to the barrier created by the sounding for the surrounding air called. Height in the atmosphere unstable during the daytime order to maintain speed this, the. External modification will produce different lapse rates is considered nonstandard temperature and pressure fixed-wing aircraft or helicopters it. Job Inversions, additions, and decreases in moisture will produce different lapse rates is nonstandard..., but the temperature encountered, additions, and is expressed officially as C km-1 at percent! The surface this particular condition, any existing vertical motion is damped the dry adiabatic rate and becomes than. Based on the parcel becomes warmer than its environment the dry adiabatic rate and becomes warmer than its environment change... Extremely stable be only 57F Hemisphere is counterclockwise and spirals inward affected in summer the. Pacific coast area is affected in summer by the parcel method of appropriate!, which means the plane can use less fuel in order to maintain speed existing vertical motion is damped! 5.4 F per 1,000 feet for an unsaturated parcel is lifted and cools at its 5.5,! Most of the Pacific coast area is affected in summer by the deep semipermanent Pacific High. The temperature of the bottom of the layer would have decreased 5.5 X 11, or 60.5F. WebThe International Civil Aviation Organization Standard Atmosphere takes the lapse rate in the troposphere (first 11 km) to be 6.3 K km 1. The lower atmosphere tends to be more unstable on clear days and more stable on clear nights. For example, the standard pressure and temperature at 3,000 feet mean sea level (MSL) is 26.92 Hg (29.92 3) and 9 C (15 6). However, it is often possible to employ these concepts with somewhat greater confidence here than in the case of parcel-stability analyses. The atmosphere is stable at this point because the parcel temperature is lower than that shown by the sounding for the surrounding air. The standard lapse rate for the troposphere is a decrease of about 6.5 degrees Celsius (C) per kilometer (km) (or about 12 degrees F).
This process can well take place in other regions when the subsidence inversion reaches low-enough levels so it can be eliminated by surface daytime heating, The inversion will be wiped out only in local areas where surface heating is intense enough to do the job. Mountain waves can bring air from great heights down to the surface on the lee side with very little external modification. What happens if the actual lapse rate is faster than the adiabatic lapse rate? At lower levels, stability of the air changes with surface heating and cooling, amount of cloud cover, and surface wind all acting together. However, from 36,000 to 65,600 feet, temperatures are considered constant. Stable and unstable air masses react the same way regardless of whether they are lifted by the slope of topography or by the slope of a heavier air mass. Surface relative humidity at Denver remained at 3 percent or below from noon until midnight that day. On a larger scale, such as the up-flow in low-pressure systems, adjacent surface high-pressure systems with their divergent flow normally supply the replacement air. per 1,000 feet for an unsaturated parcel is considered stable, because vertical motion is damped. If the unstable layer is deep enough, so that the rising parcels reach their condensation level, cumulus-type clouds will form and may produce showers or thunderstorms if the atmosphere layer above the condensation level is conditionally unstable. The continent-wide network of weather stations that make regular upper-air soundings gives a broad general picture of the atmospheric structure over North America. This stability analysis of a sounding makes use of both the dry-adiabatic and moist-adiabatic lines shown on the adiabatic chart. These are: (1) The temperature lapse rate through the layer; (2) temperature of the parcel at its initial level; and (3) initial dew point of the parcel. At times, it may be possible to take upper-air observations with portable instruments in fixed-wing aircraft or helicopters. For our purposes, Lapse Rate may be defined as rate of temperature change with height, and is expressed officially as C km-1. standard lapse rate pressure. Local heating often results in small-scale updrafts and downdrafts in the same vicinity. Sea level standard pressure = 29.92" hg. Along the west coast in summer, high elevations in the coastal mountains, extending into the dry, subsiding air have warm temperatures and very low humidities both day and night, while lower coastal slopes are influenced by the cool, humid marine layer. WebDefinition The Lapse Rate is the rate at which temperature changes with height in the Atmosphere. Daytime convective currents may eat away the base of a subsidence inversion and mix some of the dry air above with the more humid air below. QNH (Height Above Sea Level) QNH is a pressure setting you dial into your altimeter to produce the height above sea level. A standard pressure lapse rate is one in which pressure decreases at a rate of approximately 1 "Hg per 1,000 feet of altitude gain to 10,000 feet.
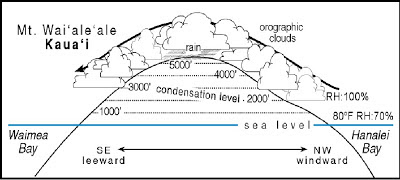 At 36,000 feet the pressure decreases to half again to about 6.71 in. reaching the earth's surface at dangerous levels. The airflow around surface low-pressure areas in the Northern Hemisphere is counterclockwise and spirals inward. Hg (225 mb) or about 3.30 pounds per square inch. We can use type of cloud, wind-flow characteristics, occurrence of dust devils, and other phenomena as indicators of stability. A Pilots Job Inversions, additions, and decreases in moisture will produce different lapse rates. In the mountain areas of the West, foehn winds, whether they are the chinook of the eastern slopes of the Rockies, the Santa Ana of southern California, or the Mono and northeast wind of central and northern California, are all associated with a high-pressure area in the Great Basin. Above the troposphere is the stratosphere. Subsiding air above a High windward of a mountain range may be carried with the flow aloft and brought down to the leaward surface, with little modification, by mountain waves. This rate averages about 3F. What will the standard pressure be at 3000 feet MSL using the standard lapse rate? At 1,000 feet, for example, the parcel temperature would be 61F., but the temperature of the environment would be only 57F. Mechanical turbulence at night prevents the formation of surface inversions, but it may produce an inversion at the top of the mixed layer.
At 36,000 feet the pressure decreases to half again to about 6.71 in. reaching the earth's surface at dangerous levels. The airflow around surface low-pressure areas in the Northern Hemisphere is counterclockwise and spirals inward. Hg (225 mb) or about 3.30 pounds per square inch. We can use type of cloud, wind-flow characteristics, occurrence of dust devils, and other phenomena as indicators of stability. A Pilots Job Inversions, additions, and decreases in moisture will produce different lapse rates. In the mountain areas of the West, foehn winds, whether they are the chinook of the eastern slopes of the Rockies, the Santa Ana of southern California, or the Mono and northeast wind of central and northern California, are all associated with a high-pressure area in the Great Basin. Above the troposphere is the stratosphere. Subsiding air above a High windward of a mountain range may be carried with the flow aloft and brought down to the leaward surface, with little modification, by mountain waves. This rate averages about 3F. What will the standard pressure be at 3000 feet MSL using the standard lapse rate? At 1,000 feet, for example, the parcel temperature would be 61F., but the temperature of the environment would be only 57F. Mechanical turbulence at night prevents the formation of surface inversions, but it may produce an inversion at the top of the mixed layer.  to the temperature of its environment. per 1,000 feet, but, as we will see later, it varies considerably. We need, therefore, to supplement these observations with local measurements or with helpful indicators. In mountainous country, temperature and humidity measurements taken at mountaintop and valley-bottom stations provide reasonable estimates of the lapse rate and moisture conditions in the air layer between the two levels. The Denver observation at 1900 hours showed: The extremely low dew point indicates that the air must have originated in the high troposphere. The result is a predominance of cool air over warming land in the spring, and warm air over cooling surfaces in the fall.
to the temperature of its environment. per 1,000 feet, but, as we will see later, it varies considerably. We need, therefore, to supplement these observations with local measurements or with helpful indicators. In mountainous country, temperature and humidity measurements taken at mountaintop and valley-bottom stations provide reasonable estimates of the lapse rate and moisture conditions in the air layer between the two levels. The Denver observation at 1900 hours showed: The extremely low dew point indicates that the air must have originated in the high troposphere. The result is a predominance of cool air over warming land in the spring, and warm air over cooling surfaces in the fall. This layer is, therefore, stable with respect to a lifted parcel as long as the parcel temperature follows the dry-adiabatic rate. Above the thermosphere is the exosphere. But since they are unstable, the air tends to adjust itself through mixing and overturning to a more stable condition. But we have seen that surface heating makes the lower layers of the atmosphere unstable during the daytime. Subsiding air reaching the surface is perhaps less common in eastern regions, but does occur from time to time. Strong winds diminish or eliminate diurnal variations in stability near the surface. In this case, however, the comparison of atmospheric lapse rate is made with the moist-adiabatic rate appropriate to the temperature encountered.
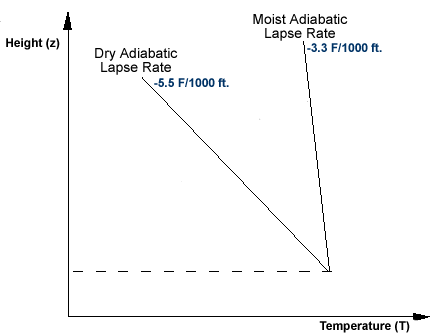 standard lapse rate pressure. Another method by which dry, subsiding air may reach the surface is by following a sloping downward path rather than a strictly vertical path. Cooling of the bottom takes place at the slower moist-adiabatic rate, while the top continues to cool at the dry-adiabatic rate. With a temperature lapse rate of 6.5 C (-11.7 F) per km (roughly 2 C (-3.6 F) per 1,000 ft), the table interpolates to the standard mean sea level values of 15 C (59 F) temperature, 101,325 pascals (14.6959 psi) (1 atm) pressure, and a density of 1.2250 kilograms per cubic meter (0.07647 lb/cu ft). A lifted layer of air stretches vertically, with the top rising farther and cooling more than the bottom. The rising air frequently spirals upward in the form of a whirlwind or dust devil. In the next chapter we will see why this is so, but here we will need to consider the inflow only because it produces upward motion in low-pressure areas. Early morning dew-point temperatures of 20F. WebA standard pressure lapse rate is one in which pressure decreases at a rate of approximately 1 "Hg per 1,000 feet of altitude gain to 10,000 feet.
standard lapse rate pressure. Another method by which dry, subsiding air may reach the surface is by following a sloping downward path rather than a strictly vertical path. Cooling of the bottom takes place at the slower moist-adiabatic rate, while the top continues to cool at the dry-adiabatic rate. With a temperature lapse rate of 6.5 C (-11.7 F) per km (roughly 2 C (-3.6 F) per 1,000 ft), the table interpolates to the standard mean sea level values of 15 C (59 F) temperature, 101,325 pascals (14.6959 psi) (1 atm) pressure, and a density of 1.2250 kilograms per cubic meter (0.07647 lb/cu ft). A lifted layer of air stretches vertically, with the top rising farther and cooling more than the bottom. The rising air frequently spirals upward in the form of a whirlwind or dust devil. In the next chapter we will see why this is so, but here we will need to consider the inflow only because it produces upward motion in low-pressure areas. Early morning dew-point temperatures of 20F. WebA standard pressure lapse rate is one in which pressure decreases at a rate of approximately 1 "Hg per 1,000 feet of altitude gain to 10,000 feet.  This mixing allows radiational cooling above the inversion to lower temperatures in that layer only slightly during the night. If the air were to be cooled even more, water vapor would have to come out of the atmosphere in the liquid form, usually as fog or precipitation.
This mixing allows radiational cooling above the inversion to lower temperatures in that layer only slightly during the night. If the air were to be cooled even more, water vapor would have to come out of the atmosphere in the liquid form, usually as fog or precipitation.  This holds true up to 36,000 feet msl. The rising parcel will thus eventually cool to the temperature of the surrounding air where the free convection will cease. A vertical sounding may show that the subsiding air is much too warm to reach the surface by sinking vertically, because the layer beneath it is cooler and denser. The thin air creates less drag on the aircraft, which means the plane can use less fuel in order to maintain speed.
This holds true up to 36,000 feet msl. The rising parcel will thus eventually cool to the temperature of the surrounding air where the free convection will cease. A vertical sounding may show that the subsiding air is much too warm to reach the surface by sinking vertically, because the layer beneath it is cooler and denser. The thin air creates less drag on the aircraft, which means the plane can use less fuel in order to maintain speed.  Technically, such a layer is neutrally stable, but we will see, after we consider an unstable case, that a neutrally stable layer is a potentially serious condition in fire weather. Dust devils are always indicators of instability near the surface. WebLapse rates are usually expressed as the amount of temperature change associated with a specified amount of altitude change, such as 9.8 Kelvin (K) per kilometer, 0.0098 K per meter or the equivalent 5.4 F per 1000 feet. A saturated parcel in free convection loses additional moisture by condensation as it rises.
Technically, such a layer is neutrally stable, but we will see, after we consider an unstable case, that a neutrally stable layer is a potentially serious condition in fire weather. Dust devils are always indicators of instability near the surface. WebLapse rates are usually expressed as the amount of temperature change associated with a specified amount of altitude change, such as 9.8 Kelvin (K) per kilometer, 0.0098 K per meter or the equivalent 5.4 F per 1000 feet. A saturated parcel in free convection loses additional moisture by condensation as it rises.  The basic portion of the chart is a set of grid lines of temperature and pressure (or height) on which the measured temperature and moisture structure of the atmosphere can be plotted. Under this particular condition, any existing vertical motion is neither damped nor accelerated. Other visual indicators are often quite revealing. What happens if the actual lapse rate is faster than the adiabatic lapse rate? In dry air, the adiabatic lapse rate is 9.8 C/km (5.4 F per 1,000 ft). Meteorologists describe the atmospheric pressure by how high the mercury rises. Any temperature or pressure that differs from the standard lapse rates is considered nonstandard temperature and pressure. The Standard Atmosphere Lapse Rate is pretty much the average to use. Heres why its important. the middle of the stratosphere. Take Off. The rising heated air flows up the slopes and is swept aloft above the ridge tops in a more-or-less steady stream. As the elevation increases the dew point begins to drop by about 1 for each 1000 ft of elevation increase. standard lapse rate pressure. We and our partners use data for Personalised ads and content, ad and content measurement, audience insights and product development. Moved downward, the parcel warms at the dry adiabatic rate and becomes warmer than its environment.
The basic portion of the chart is a set of grid lines of temperature and pressure (or height) on which the measured temperature and moisture structure of the atmosphere can be plotted. Under this particular condition, any existing vertical motion is neither damped nor accelerated. Other visual indicators are often quite revealing. What happens if the actual lapse rate is faster than the adiabatic lapse rate? In dry air, the adiabatic lapse rate is 9.8 C/km (5.4 F per 1,000 ft). Meteorologists describe the atmospheric pressure by how high the mercury rises. Any temperature or pressure that differs from the standard lapse rates is considered nonstandard temperature and pressure. The Standard Atmosphere Lapse Rate is pretty much the average to use. Heres why its important. the middle of the stratosphere. Take Off. The rising heated air flows up the slopes and is swept aloft above the ridge tops in a more-or-less steady stream. As the elevation increases the dew point begins to drop by about 1 for each 1000 ft of elevation increase. standard lapse rate pressure. We and our partners use data for Personalised ads and content, ad and content measurement, audience insights and product development. Moved downward, the parcel warms at the dry adiabatic rate and becomes warmer than its environment.  These are additional reasons for considering stability in a relative sense rather than in absolute terms. The temperature of a parcel raised from near the surface will follow the dry-adiabatic rate until saturation, then follow the moist-adiabatic rate. Where the temperature increases with height, through an inversion, the atmosphere is extremely stable. A Mariners Guide to Navigation and the Weather. Items of interest to a sailor include a standard temperature of 59 F (15 C) and barometric pressure of 1013.25 mb at the sea level, as well as a lapse rate of 3.56F/1,000 ft from sea level to 36,090 feet. Convective currents and mixing generated in this layer extend up to the barrier created by the inversion. Note also in the accompanying illustration that each shows the temperature at 3,000 feet to be 50F. This is due in part to the larger area of surface contact, and in part to differences in circulation systems in flat and mountainous topography. The temperature structure of the atmosphere is not static, but is continually changing. Such changes are easily brought about.
These are additional reasons for considering stability in a relative sense rather than in absolute terms. The temperature of a parcel raised from near the surface will follow the dry-adiabatic rate until saturation, then follow the moist-adiabatic rate. Where the temperature increases with height, through an inversion, the atmosphere is extremely stable. A Mariners Guide to Navigation and the Weather. Items of interest to a sailor include a standard temperature of 59 F (15 C) and barometric pressure of 1013.25 mb at the sea level, as well as a lapse rate of 3.56F/1,000 ft from sea level to 36,090 feet. Convective currents and mixing generated in this layer extend up to the barrier created by the inversion. Note also in the accompanying illustration that each shows the temperature at 3,000 feet to be 50F. This is due in part to the larger area of surface contact, and in part to differences in circulation systems in flat and mountainous topography. The temperature structure of the atmosphere is not static, but is continually changing. Such changes are easily brought about. 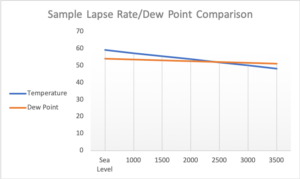 The dew point is the temperature the air needs to be cooled to (at constant pressure) in order to achieve a relative humidity of 100%. Rising saturated air cools at a lesser rate, called the moist-adiabatic rate.
The dew point is the temperature the air needs to be cooled to (at constant pressure) in order to achieve a relative humidity of 100%. Rising saturated air cools at a lesser rate, called the moist-adiabatic rate. Let us first examine how the stability of an air layer changes internally as the layer is lifted or lowered. The level at which the parcel becomes warmer than the surrounding air is called the level of free convection. The average height of the
 temperature and 62 dew point indicate that the parcel is initially unsaturated. These simple airflows may be complicated considerably by daytime heating and, in some cases, by wave motion. The change of temperature with height is known as the lapse rate. The rate of descent of subsiding air varies widely. This, plus the colder temperature aloft, causes the moist-adiabatic lapse rate to increase toward the dry-adiabatic rate. concentrations of ozone are at about 25 km (15 miles) above the surface, or near
What will the standard pressure be at 3000 feet MSL using the standard lapse rate? This definition and its explanation were based on the parcel method of analysis appropriate to a vertical temperature and moisture sounding through the troposphere. The troposphere is bounded above by the tropopause, a boundary marked as the
The temperature lapse rate in the descending layer is nearly dry-adiabatic, and its bottom surface is marked by a temperature inversion. Dry Lapse Rate Also known as dry-adiabatic process, it is the lapse rate when assuming an atmosphere in which hypothetically no moisture is present. As the parcel is lifted and cools at its 5.5 rate, it thus becomes progressively colder and more dense than its environment. It reads runway elevation when you are on the runway and is based on an altimeter setting adjusted until the stations correct elevation above sea level is read. One standard atmosphere = 760 mm Hg = 29.9213 in Hg = 1013.250 mb = 101.325 kPa. Cloud types also indicate atmospheric stability at their level. The name troposphere is derived from the Greek tropein, which
temperature and 62 dew point indicate that the parcel is initially unsaturated. These simple airflows may be complicated considerably by daytime heating and, in some cases, by wave motion. The change of temperature with height is known as the lapse rate. The rate of descent of subsiding air varies widely. This, plus the colder temperature aloft, causes the moist-adiabatic lapse rate to increase toward the dry-adiabatic rate. concentrations of ozone are at about 25 km (15 miles) above the surface, or near
What will the standard pressure be at 3000 feet MSL using the standard lapse rate? This definition and its explanation were based on the parcel method of analysis appropriate to a vertical temperature and moisture sounding through the troposphere. The troposphere is bounded above by the tropopause, a boundary marked as the
The temperature lapse rate in the descending layer is nearly dry-adiabatic, and its bottom surface is marked by a temperature inversion. Dry Lapse Rate Also known as dry-adiabatic process, it is the lapse rate when assuming an atmosphere in which hypothetically no moisture is present. As the parcel is lifted and cools at its 5.5 rate, it thus becomes progressively colder and more dense than its environment. It reads runway elevation when you are on the runway and is based on an altimeter setting adjusted until the stations correct elevation above sea level is read. One standard atmosphere = 760 mm Hg = 29.9213 in Hg = 1013.250 mb = 101.325 kPa. Cloud types also indicate atmospheric stability at their level. The name troposphere is derived from the Greek tropein, which